Products & Catalogue
Our comprehensive range of high-quality biologicals and bio-stimulants seamlessly integrates with conventional farming practices to enhance crop performance, soil health, and sustainable agricultural outcomes.
Fungi
Advanced mycorrhizal fungi formulations that enhance nutrient uptake, improve water retention, and strengthen crop resilience against environmental stresses.
Bacteria
Specialized Bacillus and Pseudomonas species that promote plant growth, enhance disease resistance, and improve overall soil health through beneficial microbial activity.
Yeast
Carefully selected yeast strains that boost plant vigor, enhance stress tolerance, and contribute to balanced soil microbiology for optimal growing conditions.
Species List
Explore our comprehensive collection of beneficial microorganisms including fungi, bacteria, and yeast species that enhance agricultural productivity and soil health.
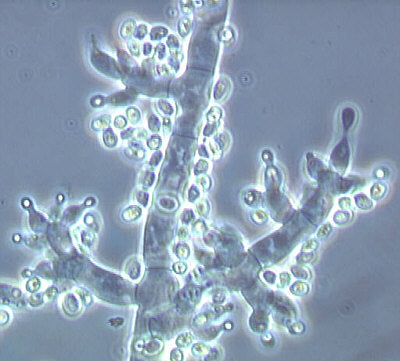
Trichoderma harzianum
Enhances root development and disease resistance
Description
A beneficial soil fungus that forms symbiotic relationships with plant roots, promoting nutrient uptake and protecting against soil-borne pathogens.
Recommended Crops
Tomatoes, peppers, cucumbers, soybeans
Key Benefits
- Improves nutrient absorption
- Increases disease resistance
- Enhances root development
- Reduces need for chemical fertilizers
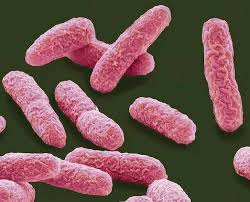
Bacillus subtilis
Natural biocontrol agent and growth promoter
Description
A gram-positive bacterium that produces antimicrobial compounds and promotes plant growth through various mechanisms.
Recommended Crops
Corn, wheat, rice, cotton
Key Benefits
- Controls plant pathogens
- Stimulates plant immunity
- Improves stress tolerance
- Increases crop yield
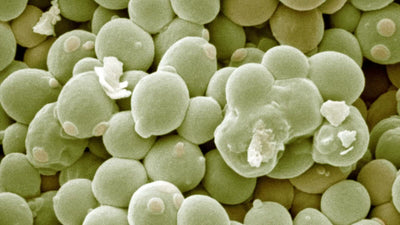
Saccharomyces cerevisiae
Soil conditioning and nutrient cycling for plants
Description
A versatile yeast that improves soil structure and enhances the availability of nutrients for plant uptake.
Recommended Crops
Vegetables, fruits, grains
Key Benefits
- Improves soil structure
- Enhances nutrient availability
- Supports beneficial microorganisms
- Increases water retention
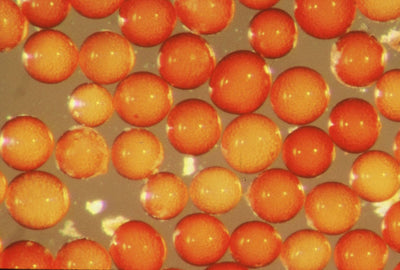
Rhizophagus irregularis
Nutrient uptake and drought tolerance
Description
A widely-distributed beneficial soil fungus that makes plants more resilient and productive.
Recommended Crops
Grains, vegetables, ornamentals, grasses
Key Benefits
- Improves soil structure
- Enhances nutrient availability
- Supports beneficial microorganisms
- Increases water retention

Funneliformis Mosseae
Nutrient uptake and drought tolerance
Description
A globally distributed arbuscular mycorrhizal fungus that forms symbiotic partnerships with plant roots. It helps plants access nutrients that are otherwise unavailable, while strengthening resilience against environmental stresses.
Recommended Crops
Grains, vegetables, ornamentals, turf, pasture, and grasses.
Key Benefits
- Improves soil structure and root health
- Enhances nutrient availability (especially phosphorus and micronutrients)
- Supports beneficial microbial activity in the rhizosphere
- Increases plant water retention and drought tolerance
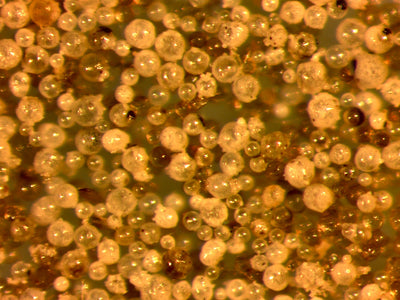
Rhizophagus aggregatus
Root growth and stress resilience
Description
A versatile arbuscular mycorrhizal fungus found in diverse soils worldwide. It forms symbiotic associations with plant roots, expanding their surface area for improved nutrient and water uptake. Known for establishing quickly and enhancing plant tolerance to stress conditions.
Recommended Crops
Vegetables, legumes, cereals, ornamentals, grasses, and fruit crops.
Key Benefits
- Promotes strong root system development
- Improves uptake of phosphorus and trace minerals
- Enhances plant tolerance to environmental stresses
- Supports overall plant vigor and soil health

Claroideoglomus etunicatum
Nutrient efficiency and broad adaptability
Description
A highly adaptable arbuscular mycorrhizal fungus known for thriving across a wide range of soils and climates. It forms mutualistic associations with plant roots, improving the efficiency of nutrient uptake and enhancing resilience under challenging field conditions.
Recommended Crops
Row crops (corn, soybeans, wheat), vegetables, fruit crops, ornamentals, turf, and forages.
Key Benefits
- Improves phosphorus and micronutrient availability
- Increases overall nutrient-use efficiency
- Enhances plant tolerance to soil and environmental stresses
- Widely adaptable, making it effective across many crop systems
Claroideoglomus claroideum
Phosphorus uptake and stress adaptation
Description
A beneficial arbuscular mycorrhizal fungus valued for its ability to boost phosphorus uptake and help plants perform under nutrient-poor or stressful conditions. It is often used in agricultural and horticultural systems to improve crop establishment and resilience.
Recommended Crops
Vegetables, legumes, grains, fruit crops, ornamentals, and turf.
Key Benefits
- Improves phosphorus and micronutrient absorption
- Supports healthy root development
- Enhances plant performance in low-fertility soils
- Increases tolerance to drought and other stresses
Azotobacter chroococcum
Nitrogen fixation and soil vitality
Description
A free-living, nitrogen-fixing bacterium commonly found in soils. It converts atmospheric nitrogen into plant-available forms, while also producing growth-promoting substances such as vitamins, auxins, and gibberellins. Known for supporting soil fertility and improving overall plant vigor.
Recommended Crops
Cereals, vegetables, legumes, fruit crops, ornamentals, and turf.
Key Benefits
- Fixes atmospheric nitrogen into usable plant forms
- Produces natural growth-promoting hormones
- Improves seed germination and root development
- Enhances soil fertility and microbial diversity
- Boosts crop productivity under low-input conditions
Bacillus licheniformis
Nutrient cycling and plant defense
Description
A resilient, spore-forming bacterium widely found in soil and plant environments. It contributes to nutrient cycling by solubilizing phosphorus and producing enzymes that break down organic matter. B. licheniformis also produces antimicrobial compounds that help protect plants from soil-borne pathogens.
Recommended Crops
Vegetables, cereals, legumes, fruit crops, ornamentals, and turf.
Key Benefits
- Solubilizes phosphorus and other key nutrients
- Produces enzymes that enhance soil fertility
- Supports natural plant defenses against pathogens
- Improves root growth and nutrient uptake
- Contributes to healthier, more resilient soils
Pseudomonas aureofaciens
Root vitality and nutrient dynamics
Description
A beneficial rhizobacterium that thrives in the root zone and supports overall soil health. It is recognized for producing metabolites that contribute to a balanced soil environment and for enhancing plant nutrient dynamics.
Recommended Crops
Vegetables, cereals, legumes, fruit crops, ornamentals, turf, and greenhouse crops.
Key Benefits
- Supports healthy root-zone conditions
- Contributes to balanced soil microbial activity
- Enhances nutrient availability and uptake
- Promotes overall plant vigor and resilience

Paenibacillus durum
Nutrient availability and soil balance
Description
A naturally occurring soil bacterium associated with healthy root environments. It contributes to soil nutrient cycling and helps maintain a balanced microbial community that supports plant growth.
Recommended Crops
Cereals, legumes, vegetables, fruit crops, turf, and ornamentals.
Key Benefits
- Contributes to nutrient cycling in the soil
- Enhances root-zone microbial diversity
- Supports plant access to essential minerals
- Promotes resilient plant growth under variable conditions

Bacillus amyloliquefaciens
Soil fertility and plant vigor
Description
A naturally occurring, spore-forming bacterium widely present in soils and plant environments. It contributes to soil fertility through organic matter breakdown and supports healthy root development by producing enzymes and beneficial metabolites that improve nutrient dynamics.
Recommended Crops
Vegetables, cereals, legumes, fruit crops, ornamentals, turf, and greenhouse crops.
Key Benefits
- Improves nutrient availability through organic matter decomposition
- Contributes to soil fertility and structure
- Supports vigorous root development
- Enhances overall plant growth and resilience
Bacillus pumilus
Soil balance and root development
Description
A hardy, spore-forming bacterium that naturally occurs in soils and the plant rhizosphere. It is known for producing enzymes that help recycle organic matter, improving nutrient dynamics and contributing to healthier root-zone conditions.
Recommended Crops
Vegetables, cereals, legumes, fruit crops, ornamentals, turf, and greenhouse systems.
Key Benefits
- Contributes to organic matter decomposition and nutrient cycling
- Supports beneficial microbial balance in the rhizosphere
- Promotes healthy root establishment
- Enhances overall plant vigor under diverse soil conditions
Bacillus azotoformans
Nitrogen cycling and soil vitality
Description
A naturally occurring, spore-forming bacterium that contributes to soil nitrogen dynamics. It supports a balanced root-zone environment by participating in nutrient cycling and interacting with other beneficial microorganisms.
Recommended Crops
Cereals, legumes, vegetables, fruit crops, ornamentals, turf, and forage systems.
Key Benefits
- Contributes to nitrogen cycling in the soil
- Enhances microbial diversity and soil balance
- Supports healthy root development
- Promotes resilient plant growth across cropping systems
Bacillus megaterium
Nutrient availability and soil support
Description
A large, spore-forming bacterium commonly found in soils and plant environments. It is recognized for its role in nutrient transformation, particularly phosphorus solubilization, and for helping maintain a balanced microbial community in the root zone.
Recommended Crops
Vegetables, cereals, legumes, fruit crops, ornamentals, turf, and forage systems.
Key Benefits
- Contributes to phosphorus solubilization and nutrient cycling
- Supports soil microbial diversity
- Promotes healthy root-zone conditions
- Enhances overall plant vigor and resilience
